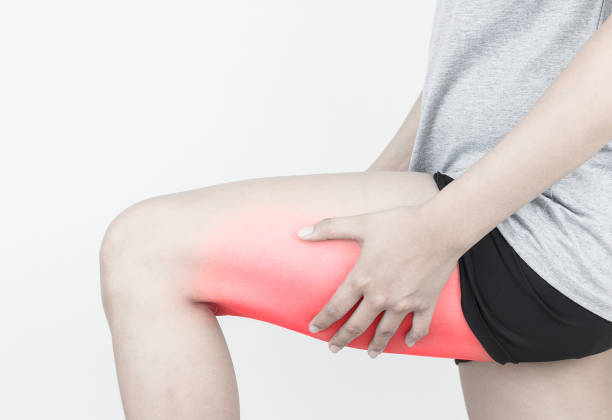
Pulling a hamstring or a “hammy” can be a painful injury with a long recovery time if not treated and diagnosed properly.
What is a Hamstring Injury?
A hamstring injury is a muscle strain or tear in the hamstring muscle.
Symptoms
A hamstring injury usually causes a sudden and sharp pain in the back of the thigh. Other symptoms include:
- Bruising of the area
- Tenderness in the back of the thigh
- Swelling
- Weakness in the leg
Causes of Hamstring Injuries
Athletes who play sports with a lot of sprints and stops such as basketball, soccer or tennis are more likely to suffer a hamstring injury. That being said, anyone can suffer from a hamstring injury. One can even pull a hamstring muscle while doing a simple task such as reaching to pick something up if their hamstrings are overly tight.
The most common ways people injure their hamstrings are:
- Sports injuries caused by extreme stretching or overloading during the sport.
- Poor Flexibility. Certain everyday movements may stretch your tight hamstrings too far.
- Muscle Overload by overtraining can cause tears.
- Sudden slip on icy or wet surfaces
Types of Hamstring Injuries
There are three classes of hamstring injuries, you will need to speak to a medical professional to have your injury properly diagnosed:
- Grade 1- Mild Strain
- Grade 2- Partial Tear
- Grade 3- Full Muscle Tear
Recovery Time
The majority of hamstring injuries are attributed to sports injuries and the length of recovery time can differ from person to person. On average a hamstring injury can take 4 to 8 weeks for partial tears and up to 3 months for complete tears.
Treatment
Most muscle injuries start with the same suggested treatment, rest, ice, compression, elevation or RICE. For more serious hamstring injuries your doctor might suggest an MRI or an ultrasound to determine the extent of the tear. There are a number of ways you can treat a mild hamstring injury:
- Rest and reduce your activity level especially in the first 48-72 hours after your injury. Use ice to help with the swelling and inflammation.
- Slow stretching to increase the range of motion in the muscles once past the initial inflammatory phase.
- Gradually add strengthening exercises to regain the strength in the injured hamstring once you are given the go ahead by your physiotherapist.
There are everyday things you can do to prevent hamstring injuries and other muscle injuries. Stretching everyday, including stretching the hamstrings, can keep the body loose and less vulnerable to muscle tears and pulls. Warm up before playing sports, especially those sports that involve sudden sprints and stops.
If you have been injured and want to see a physiotherapist. Call the professionals at Durham Orthopedic Sports & Injury Clinic at 905-428-7800.

