Physiotherapists play a crucial role in helping people recover from injuries, manage pain, and regain mobility. Whether you’re an athlete, a busy professional, or an aging adult, physiotherapy can make a significant difference in your recovery. Here are the top 10 common injuries treated by physiotherapists and how they can help you get back to your best.
1. Back Pain
Back pain is one of the most common complaints, often caused by poor posture, muscle strain, or spinal conditions, such as disc herniations or degenerative disc disease.
Physiotherapy Helps By Providing:
- Education on postural corrections and ergonomic advice to decrease the strain on your back.
- Manual therapy to decrease stiffness and improve mobility.
- Customized exercise programs to strengthen the back and core.
2. Knee Injuries
From ACL tears to patellar tendinitis, knee injuries can affect mobility and quality of life.
Physiotherapy Helps By Providing:
- Strengthening exercises for supporting muscles to decrease the strain on the knee joint.
- Balance and stability training.
- Education on techniques to reduce swelling and pain.
3. Shoulder Injuries
Conditions like rotator cuff injuries and frozen shoulder are common in people with repetitive overhead movements or poor posture.
Physiotherapy Helps by providing:
- Manual therapy to restore mobility.
- Strength training for shoulder stability.
- Modalities like ultrasound therapy to reduce inflammation.
4. Sprained Ankles
Ankle sprains are frequent in sports or uneven terrain walking and can lead to long term instability if not treated.
Physiotherapy Helps by providing:
- Rehabilitation exercises to restore strength and balance.
- Taping or bracing techniques to prevent further injury.
- Gait retraining to improve walking patterns.
5. Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)
This overuse injury affects the tendons in the elbow, causing pain and reduced grip strength.
Physiotherapy Helps by providing:
- Stretching and strengthening exercises.
- Manual therapy to reduce tension in the forearm muscles.
- Advice on activity modification to prevent recurrence.
6. Plantar Fasciitis
Heel pain caused by inflammation of the plantar fascia is a common issue for runners and people who stand for long hours.
Physiotherapy Helps By providing:
- Stretching exercises for the foot and calf.
- Manual therapy to improve tissue mobility.
- Advice on footwear and orthotics.
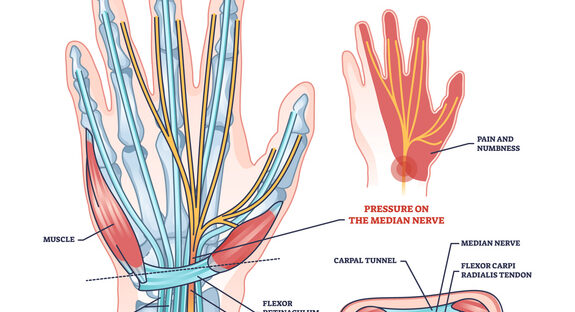
7. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
This condition is caused by pressure on the median nerve in the wrist, leading to numbness and pain in the hand.
Physiotherapy Helps By Providing:
- Nerve gliding exercises to reduce compression.
- Wrist splinting for nighttime relief.
- Strengthening and flexibility exercises.
8. Hip Pain
Hip injuries, such as bursitis or labral tears, are common in active individuals and older adults.
Physiotherapy Helps By Providing:
- Exercises to strengthen surrounding muscles.
- Manual therapy to improve joint mobility.
- Gait analysis to identify and correct movement patterns.
9. Whiplash
A sudden jerking motion, often from car accidents, can cause neck strain and stiffness.
Physiotherapy Helps By Providing:
- Gentle range of motion exercises and manual therapy techniques to restore mobility.
- Pain management techniques such as acupuncture.
- Postural advice to support recovery.
10. Fractures
Recovering from a fracture involves more than just waiting for the bone to heal.
Physiotherapy Helps By Providing:
- Strengthening exercises to restore muscle function.
- Joint mobilizations to reduce stiffness and improve mobility.
- Balance and coordination training.
Why Choose Physiotherapy for Injury Recovery?
Physiotherapy is not just about pain relief, it’s about treating the root cause of the problem and preventing future injuries. By working with a qualified physiotherapist, you can:
- Speed up recovery.
- Regain strength and mobility.
- Reduce the likelihood of reinjury.
At Durham Orthopedic & Sports Injury Clinic, we specialize in treating a wide range of injuries. Our team of experienced physiotherapists and massage therapists will create a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs. Whether you’re dealing with a sports injury, work related pain, or a chronic condition, we’re here to help you recover and thrive.
Contact us today to book your appointment and start your road to recovery today!